Corporate tax in Oman is a direct tax levied on the profits of businesses operating within the Sultanate, governed by the Income Tax Law (Royal Decree No. 28/2009, amended by Royal Decree No. 118/2020). It applies to Omani companies, foreign entities with a permanent establishment (PE) in Oman, and certain partnerships or joint ventures conducting taxable activities. The tax is designed to generate revenue for the government, supporting public services and economic diversification away from oil dependency.
- Taxable Income: Includes revenue from business operations, capital gains, dividends, and other income sources, minus allowable deductions (e.g., operating expenses, depreciation). For example, a manufacturing company in Muscat earning OMR 100,000 in revenue with OMR 40,000 in deductible costs would pay tax on OMR 60,000.
- Standard Rate: 15% applies to most entities, including Omani companies and foreign PEs. Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) meeting specific criteria (e.g., registered capital up to OMR 60,000, gross income up to OMR 150,000, and fewer than 25 employees) enjoy a reduced 3% rate.
- Petroleum Sector: Companies involved in petroleum sales face a 55% rate, determined by Exploration and Production Sharing Agreements (EPSAs) with the government.
- Exemptions: Certain sectors, like industrial activities, may qualify for temporary tax holidays under economic stimulus plans, though most exemptions (e.g., for mining or tourism) were phased out in 2017.
Oman’s corporate tax system is straightforward, with no regional or local income taxes, making it attractive for businesses. However, compliance—filing returns, maintaining IFRS-compliant accounts, and meeting deadlines—is mandatory, driving the need for expert services.
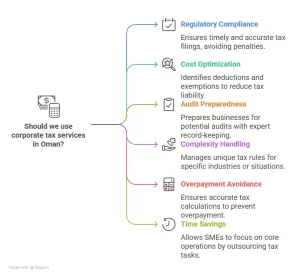
Why Do You Need Corporate Tax Services in Oman?
Corporate tax services are essential in Oman due to the complexity, legal obligations, and financial implications of the tax regime:
- Regulatory Compliance: Businesses must file annual tax returns within four months of the fiscal year-end (e.g., April 30 for a December 31 close) with audited accounts per International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Non-compliance risks penalties from OMR 100 to OMR 2,000, plus 1% monthly interest on unpaid tax.
- Cost Optimization: Services help identify deductions, exemptions, or SME benefits (e.g., 3% rate), reducing tax liability. A retailer with OMR 120,000 income might lower its tax from OMR 18,000 (15%) to OMR 3,600 (3%) with proper structuring.
- Audit Preparedness: The Oman Tax Authority (OTA) can assess taxes up to three years after filing (five if no return is submitted), making expert record-keeping and audit defense critical.
- Complexity of Special Cases: Petroleum companies (55% rate), foreign PEs, or entities in special economic zones (e.g., Duqm) face unique rules, requiring specialized knowledge.
- Avoiding Overpayment: Misinterpreting taxable income or missing foreign tax credits (for worldwide income) can inflate tax bills. Services ensure accurate calculations.
- Time and Resource Savings: SMEs or startups often lack in-house tax expertise, making outsourcing to professionals a practical choice to focus on core operations.
For instance, a logistics firm might hire tax services to avoid an OTA penalty for late filing while ensuring it claims all allowable expenses, saving both money and hassle.
All-in-One Corporate Tax Solutions in Oman
An all-in-one corporate tax solution in Oman integrates multiple services into a seamless package, addressing every aspect of tax management:
- Tax Planning: Strategizing to minimize liability, such as leveraging SME status or carrying forward losses (allowed under recent reforms). E.g., a company with a OMR 20,000 loss in 2024 could offset it against 2025 profits.
- Return Preparation and Filing: Compiling financials, calculating tax, and submitting returns electronically via the OTA portal, ensuring deadlines are met.
- Audit Support: Preparing IFRS-compliant accounts and defending against OTA audits, which can revisit three to five years of records.
- Compliance Monitoring: Tracking changes in tax laws (e.g., 2020 amendments on residency or information exchange) and ensuring adherence.
- Advisory Services: Guiding on sector-specific rules (e.g., 55% petroleum tax) or international tax treaties to avoid double taxation.
- Technology Integration: Using software for real-time tax tracking, payment scheduling, and record retention (required for five years, or 15 for real estate).
A construction company, for example, could use an all-in-one solution to file its OMR 200,000 income return, claim deductions for equipment, and prepare for a potential OTA review—all handled by one provider, reducing complexity and cost.
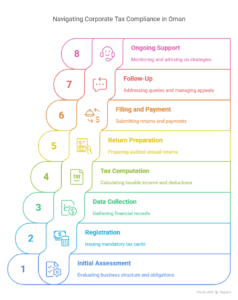
Procedure of Corporate Tax Services in Oman
The procedure for corporate tax services in Oman follows a structured workflow to ensure compliance and efficiency:
- Initial Assessment: The service provider reviews your business—turnover, industry, structure (e.g., LLC, PE)—to determine tax obligations and opportunities (e.g., SME rate eligibility).
- Registration: If unregistered, they assist with OTA tax card issuance, mandatory for all taxpayers since 2017, submitting commercial registration and financial details.
- Data Collection: Gathering financial records—revenue, expenses, assets—for the fiscal year (typically January 1 to December 31, unless approved otherwise).
- Tax Computation: Calculating taxable income, applying the correct rate (15%, 3%, or 55%), and identifying deductions or credits. E.g., a firm with OMR 80,000 income and OMR 20,000 expenses pays 15% on OMR 60,000 (OMR 9,000).
- Return Preparation: Preparing the annual return with audited accounts (signed by an Oman-registered auditor) in OMR, unless foreign currency is pre-approved.
- Filing and Payment: Submitting the return electronically by the deadline (e.g., April 30) and paying tax via bank transfer or OTA channels.
- Follow-Up: Addressing OTA queries, managing appeals (within 45 days to the Primary Court), and retaining records for five years.
- Ongoing Support: Monitoring quarterly instalments (if required) and advising on future tax strategies.
For an SME, this might mean filing a simplified income statement by March 31 (three months for 3% taxpayers) and paying OMR 900 on OMR 30,000 taxable income, all streamlined by the service provider.
Corporate Tax Services in Oman by Xact Auditing
Xact Auditing offers tailored corporate tax services in Oman, leveraging regional expertise and a client-focused approach:
- Tax Registration: Xact assists with OTA tax card applications, ensuring SMEs (up to OMR 150,000 income) or larger firms (15% rate) are correctly enrolled. They handle documentation like commercial registration and turnover proof.
- Compliance and Filing: They prepare and file returns, ensuring IFRS compliance and timely submission (e.g., April 30). For a petroleum firm, they navigate the 55% EPSA-based rate, filing within four months.
- Tax Planning: Xact optimizes liability—e.g., securing the 3% SME rate for a qualifying LLC with OMR 50,000 capital and 10 employees, saving OMR 3,600 versus OMR 4,500 at 15%.
- Audit Defense: They conduct internal reviews and represent clients during OTA audits, maintaining five-year records (15 for real estate) to avoid penalties like OMR 2,000 for late filing.
- Technology Tools: Xact uses OTA-compliant software for accurate tax tracking and reporting, ideal for complex cases like foreign PEs with worldwide income.
- Sector Expertise: They specialize in industries like oil and gas (55% rate), manufacturing (potential exemptions), and SMEs, offering bespoke advice.
- Responsive Support: Xact provides quick responses to OTA notices or client queries, critical when facing a 1% monthly interest penalty on unpaid tax.
For example, a Duqm-based exporter might use Xact to register, file a OMR 100,000 income return at 15% (OMR 15,000), and appeal an OTA adjustment, all while benefiting from their GCC experience (e.g., UAE tax since 2018) and competitive pricing for Oman’s SME market.
Corporate tax in Oman, with its 15% standard rate, 3% SME relief, and 55% petroleum tax, requires careful management to ensure compliance and savings. Xact Auditing’s comprehensive services—from registration to audit support—make them a strong choice, blending expertise, technology, and tailored solutions. Whether you’re an SME or a multinational, their approach simplifies the process while maximizing benefits. Need more details on Xact’s offerings or your specific case? Let me know!
